Evolutionary Tree
| Division: Eumycota (septate fungi) | ||||||
| Subdivision: Ascomycotina | ||||||
| Class: Euascomycetes | ||||||
| Subclass: Leotiomycetidae. | ||||||
| Order: Helotiales | ||||||
| Family: Bulgariaceae Family: Cyttariaceae Family: Leotiaceae Family: Geoglossaceae Family: Helotiaceae Family: Vibrisseaceae |
||||||
| Subclass: Pezizomycetidae | ||||||
| Order: Pezizales | ||||||
| Family: Discinaceae Family: Pezizaceae Family: Pyronemataceae Family: Sarcoscyphaceae Family: Sarcosomataceae |
||||||
| Subclass: Pyrenomycetidae | ||||||
| Order: Xylariales | ||||||
| Family: Xylariacea | ||||||
| Order: Hypocreales | ||||||
|
Family: Hypocreaceae Family: Clavicipitaceae |
||||||
| Order: Sordariales | ||||||
| Family: Lasiosphaeriaceae | ||||||
| Order: Eurotiales | ||||||
| Family: Trichocomaceae | ||||||
| Subdivision: Basidiomycotina | ||||||
| Class: Hymenomycetes | ||||||
| Subclass: Holobasidiomycetidae (Homobasidiomycete Fungi) (substantial mushrooms) |
||||||
| Order: Agaricales | ||||||
| Family: Agaricaceae Family: Bolbitiaceae Family: Clavariaceae Family: Coprinaceae Family: Cortinariaceae Family: Entolomataceae Family: Hydnangiaceae Family: Marasmiaceae Family: Pleurotaceae Family: Pluteaceae Family: Schizophyllaceae Family: Strophariaceae Family: Tricholomataceae |
||||||
| Order: Boletales | ||||||
| Family: Boletaceae Family: Boletinellaceae Family: Calostomataceae Family: Gyrodontaceae Family: Paxillaceae Family: Rhizopogonaceae Family: Sclerodermataceae Family: Suillaceae |
||||||
| Order: Cantharellales | ||||||
| Family: Cantharellaceae Family: Clavulinaceae Family: Hydnaceae |
||||||
| Order: Dacrymycetales | ||||||
| Family: Dacrymycetales | ||||||
| Order: Gomphales | ||||||
|
Family: Gomphaceae Family: Hysterangiaceae Family: Phallaceae |
||||||
| Order: Hymenochaetales | ||||||
| Family: Hymenochaetaceae | ||||||
| Order: Polyporales | ||||||
| Family: Ganodermataceae Family: Gloeophyllaceae Family: Meripilaceae Family: Podoscyphaceae Family: Polyporaceae Family: Steccherinaceae |
||||||
| Order: Russulales | ||||||
| Family: Auriscalpiaceae Family: Corticiaceae Family: Hericiaceae Family: Meruliaceae Family: Rusulaceae Family: Stereaceae |
||||||
| Order: Thelephorales | ||||||
Family: Bankeraceae |
||||||
| Subclass: Phragmobasidiomycetidae (Heterobasidiomycete Fungi) |
||||||
| Order: Auriculariales | ||||||
| Family: Auriculariaceae | ||||||
| Order: Tremellales | ||||||
| Family: Exidiaceae Family: Tremellaceae Family: Tremellodendropsidaceae |
||||||
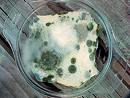 Are the only class of fungi whose mycelium is normally aseptate. Septate typically only form to delineate reproductive structures or to isolate damaged portions of mycelium. They reproduce by either sexual or asexual means and have simple reproductive bodies then Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes. Most are moulds e.g. pin mould, as seen on bread.
Are the only class of fungi whose mycelium is normally aseptate. Septate typically only form to delineate reproductive structures or to isolate damaged portions of mycelium. They reproduce by either sexual or asexual means and have simple reproductive bodies then Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes. Most are moulds e.g. pin mould, as seen on bread. A lichen is not a single organism, but rather it's a combination of two organisms which live together intimately. Most of the lichen is composed of fungal filaments, but living among the filaments are algal cells. See the Forest Lichen pages
A lichen is not a single organism, but rather it's a combination of two organisms which live together intimately. Most of the lichen is composed of fungal filaments, but living among the filaments are algal cells. See the Forest Lichen pages|
|